In Figure 16.21, 12![]() ×
×![]() 10–5 W of sound power passes perpendicularly through the surfaces labeled 1 and 2. These surfaces have areas of A1
10–5 W of sound power passes perpendicularly through the surfaces labeled 1 and 2. These surfaces have areas of A1![]() =
=![]() 4.0 m2 and A2
4.0 m2 and A2![]() =
=![]() 12 m2. Determine the sound intensity at each surface and discuss why listener 2 hears a quieter sound than listener 1.
12 m2. Determine the sound intensity at each surface and discuss why listener 2 hears a quieter sound than listener 1.
Reasoning The sound intensity I is the sound power P passing perpendicularly through a surface divided by the area A of that surface. Since the same sound power passes through both surfaces and surface 2 has the greater area, the sound intensity is less at surface 2.
|
Solution The sound intensity at each surface follows from Equation 16.8:
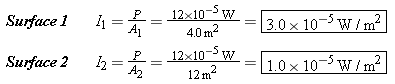 |