Conceptual Questions |
| |||
ssm Solution is in the Student Solutions Manual.
| 1 |
Why do you lunge forward when your car suddenly comes to a halt? Why are you pressed backward against the seat when your car rapidly accelerates? In your explanation, refer to the most appropriate one of Newton’s three laws of motion.
| |
| 2 |
A bird feeder of large mass is hung from a tree limb, as the drawing shows. A cord attached to the bottom of the feeder has been left dangling free. Curiosity gets the best of a child, who pulls on the dangling cord in an attempt to see what’s in the feeder. The dangling cord is cut from the same source as the cord attached to the limb. Is the cord between the feeder and the limb more likely to snap with a slow continuous pull or a sudden downward pull? Give your reasoning.
| |
| 3 |
ssm The net external force acting on an object is zero. Is it possible for the object to be traveling with a velocity that is not zero? If your answer is yes, state whether any conditions must be placed on the magnitude and direction of the velocity. If your answer is no, provide a reason for your answer.  | |
| 4 |
Is a net force being applied to an object when the object is moving downward (a) with a constant acceleration of 9.80 m/s2 and (b) with a constant velocity of 9.80 m/s? Explain.
| |
| 5 |
Newton’s second law indicates that when a net force acts on an object, it must accelerate. Does this mean that when two or more forces are applied to an object simultaneously, it must accelerate? Explain.
| |
| 6 |
A father and his seven-year-old daughter are facing each other on ice skates. With their hands, they push off against one another. (a) Compare the magnitudes of the pushing forces that they experience. (b) Which one, if either, experiences the larger acceleration? Account for your answers.
| |
| 7 |
A gymnast is bouncing on a trampoline. After a high bounce the gymnast comes down and hits the elastic surface of the trampoline. In so doing the gymnast applies a force to the trampoline. (a) Describe the effect this force has on the elastic surface. (b) The surface applies a reaction force to the gymnast. Describe the effect that this reaction force has on the gymnast.
| |
| 8 |
According to Newton’s third law, when you push on an object, the object pushes back on you with an oppositely directed force of equal magnitude. If the object is a massive crate resting on the floor, it will probably not move. Some people think that the reason the crate does not move is that the two oppositely directed pushing forces cancel. Explain why this logic is faulty and why the crate does not move.
| |
| 9 |
Three particles have identical masses. Each particle experiences only the gravitational forces due to the other two particles. How should the particles be arranged so each one experiences a net gravitational force that has the same magnitude? Give your reasoning.
| |
| 10 |
When a body is moved from sea level to the top of a mountain, what changes—the body’s mass, its weight, or both? Explain.
| |
| 11 |
The force of air resistance acts to oppose the motion of an object moving through the air. A ball is thrown upward and eventually returns to the ground. (a) As the ball moves upward, is the net force that acts on the ball greater than, less than, or equal to its weight? Justify your answer. (b) Repeat part (a) for the downward motion of the ball.
| |
| 12 |
Object A weighs twice as much as object B at the same spot on the earth. Would the same be true at a given spot on Mars? Account for your answer.
| |
| 13 |
Does the acceleration of a freely falling object depend to any extent on the location—that is, whether the object is on top of Mt. Everest or in Death Valley, California? Explain.
| |
| 14 |
A “bottle rocket” is a type of fireworks that has a long thin tail that you insert into an empty bottle, to provide a launch platform. One of these rockets is fired with the bottle pointing vertically upward. An identical rocket is fired with the bottle lying on its side, pointing horizontally. In which case does the rocket leave the bottle with the greater acceleration? Explain, ignoring air resistance and friction.
| |
| 15 |
A 10-kg suitcase is placed on a scale that is in an elevator. Is the elevator accelerating up or down when the scale reads (a) 75 N and (b) 120 N? Justify your answers.
| |
| 16 |
ssm A stack of books whose true weight is 165 N is placed on a scale in an elevator. The scale reads 165 N. Can you tell from this information whether the elevator is moving with a constant velocity of 2 m/s upward or 2 m/s downward or whether the elevator is at rest? Explain.
| |
| 17 |
Suppose you are in an elevator that is moving upward with a constant velocity. A scale inside the elevator shows your weight to be 600 N. (a) Does the scale register a value that is greater than, less than, or equal to 600 N during the time when the elevator slows down as it comes to a stop? (b) What is the reading when the elevator is stopped? (c) How does the value registered on the scale compare to 600 N during the time when the elevator picks up speed again on its way back down? Give your reasoning in each case.
| |
| 18 |
A person has a choice of either pushing or pulling a sled at a constant velocity, as the drawing illustrates. Friction is present. If the angle 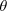 is the same in both cases, does it require less force to push or to pull? Account for your answer. is the same in both cases, does it require less force to push or to pull? Account for your answer. | |
| 19 |
Suppose that the coefficients of static and kinetic friction have values such that
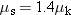 for a crate in contact with a cement floor. Does this mean that the magnitude of the static frictional force acting on the crate at rest would always be 1.4 times the magnitude of the kinetic frictional force acting on the moving crate? Give your reasoning. for a crate in contact with a cement floor. Does this mean that the magnitude of the static frictional force acting on the crate at rest would always be 1.4 times the magnitude of the kinetic frictional force acting on the moving crate? Give your reasoning. | |
| 20 |
A box rests on the floor of an elevator. Because of static friction, a force is required to start the box sliding across the floor when the elevator is (a) stationary, (b) accelerating upward, and (c) accelerating downward. Rank the forces required in these three situations in ascending order—that is, smallest first. Explain.
| |
| 21 |
A rope is used in a tug-of-war between two teams of five people each. Both teams are equally strong, so neither team wins. An identical rope is tied to a tree, and the same ten people pull just as hard on the loose end as they did in the contest. In both cases, the people pull steadily with no jerking. Which rope, if either, is more likely to break? Justify your answer.
| |
| 22 |
A stone is thrown from the top of a cliff. As the stone falls, is it in equilibrium? Explain, ignoring air resistance.
| |
| 23 |
ssm Can an object ever be in equilibrium if the object is acted on by only (a) a single nonzero force, (b) two forces that point in mutually perpendicular directions, and (c) two forces that point in directions that are not perpendicular? Account for your answers.
| |
| 24 |
A circus performer hangs stationary from a rope. She then begins to climb upward by pulling herself up, hand over hand. When she starts climbing, is the tension in the rope less than, equal to, or greater than it is when she hangs stationary? Explain.
| |
| 25 |
During the final stages of descent, a sky diver with an open parachute approaches the ground with a constant velocity. The wind does not blow him from side to side. Is the sky diver in equilibrium and, if so, what forces are responsible for the equilibrium?
| |
| 26 |
A weight hangs from a ring at the middle of a rope, as the drawing illustrates. Can the person who is pulling on the right end of the rope ever make the rope perfectly horizontal? Explain your answer in terms of the forces that act on the ring. 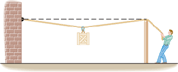 | |
| 27 |
A freight train is accelerating on a level track. Other things being equal, would the tension in the coupling between the engine and the first car change if some of the cargo in the last car were transferred to any one of the other cars? Account for your answer.
| |
| Copyright © 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. |