2.6. Freely Falling Bodies
In the absence of air resistance, it is found that all bodies near the surface of the earth fall vertically with the same acceleration. The acceleration of a freely falling body is called the acceleration due to gravity, and its magnitude is given by the symbol "g". This acceleration is always directed downward, toward the center of the earth. Near the surface of the earth g is approximately constant and has a value of
A ball is dropped from the top of a 123 m high cliff. Ignoring air resistance find the final velocity of the ball, and the amount of time it takes for it to hit the ground below.
The final velocity can be obtained using equation (2.9) and taking the direction of motion as the y direction.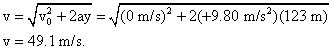 |
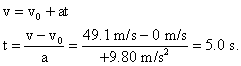 |