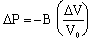Chapter Summary
PREVIEW
In this chapter you will study the elastic properties of materials and the kinds of deformations a material can experience when subjected to outside forces. A special case, the spring, will be examined in detail. You will also study simple harmonic motion, the oscillatory motion that occurs when the restoring force of an ideal spring acts on an object.
QUICK REFERENCE
Important Terms
Ideal Spring
A spring which behaves according to the relationship FApplied = kx and which has no internal friction.
Restoring Force
A force which tends to restore an object to its original state. For example, the force which tends to pull a stretched spring back to its unstretched or "equilibrium" position.
Simple Harmonic Motion
The oscillatory motion that results when an elastic material is subjected to the restoring force of an ideal spring
Period
The time required to complete one oscillatory cycle of motion.
Frequency
The number of cycles of oscillatory motion that occurs in one second
Amplitude
The maximum distance that an oscillating object moves away from its equilibrium position.
Elasticity
The tendency for a solid object to return to its original shape after it has been stretched, compressed, or otherwise distorted by outside forces
Young's Modulus
The proportionality constant which relates the fractional change in length of a material to the force per unit area applied to the material.
Shear Modulus
The proportionality constant which relates the shear deformation per unit length of a material to the force per unit area applied to the material
Bulk Modulus
The proportionality constant which relates the fractional change in volume of a material to the pressure applied to the material.
Stress
The magnitude of the force per unit area required to cause an elastic deformation.
Strain
The fractional change in length or volume that results from an applied force.
Hooke's Law
The relationship which states that stress is directly proportional to strain.
Equations
Hooke's law restoring force for an ideal spring:
| F = - kx | (10.2) |  |
The displacement of an object moving with simple harmonic motion is:
| x = A cos wt | (10.3) |  |
The velocity of an object moving with simple harmonic motion is:
| v = - Aw sin wt | (10.7) |  |
The acceleration of an object moving with simple harmonic motion is:
| a = - Aw
2 cos wt | (10.9) |  |
The equation for stretching or compression is:
 | (10.17) |  |
The equation for shear deformation is:
 | (10.18) |  |
The fractional volume change is given by:
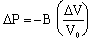 | (10.20) |  |
 |
| Copyright © 2000-2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. or related companies. All rights reserved. |