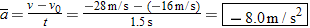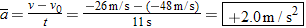A skydiver is falling straight down, along the negative y direction. (a) During the initial part of the fall, her speed increases from 16 to 28 m/s in 1.5 s, as in Figure 2.25a. (b) Later, her parachute opens, and her speed decreases from 48 to 26 m/s in 11 s, as in part b of the drawing. In both instances, determine the magnitude and direction of her average acceleration.
 |
|
Is her average acceleration positive or negative when her speed is increasing?
Since her speed is increasing, the acceleration vector must point in the same direction as the velocity vector, which points in the negative y direction. Thus, the acceleration is negative.Is her average acceleration positive or negative when her speed is decreasing?
Since her speed is decreasing, the acceleration vector must point opposite to the velocity vector. Since the velocity vector points in the negative y direction, the acceleration must point in the positive y direction. Thus, the acceleration is positive.Solution
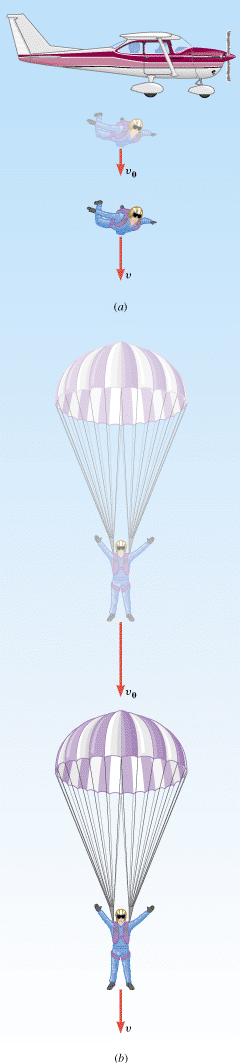
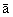 is the change in the velocity divided by the elapsed time:
is the change in the velocity divided by the elapsed time: