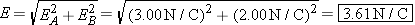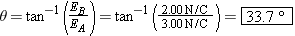|
Figure 18.18 shows two charged objects, A and B. Each contributes as follows to the net electric field at point P: EA = = 3.00 N/C directed to the right, and EB 3.00 N/C directed to the right, and EB = = 2.00 N/C directed downward. Thus, EA and EB are perpendicular. What is the net electric field at P? 2.00 N/C directed downward. Thus, EA and EB are perpendicular. What is the net electric field at P?
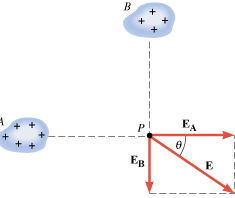 | | Figure 18.18
The electric field contributions EA and EB, which come from the two charge distributions, are added vectorially to obtain the net field E at point P. |
|
Reasoning
The net electric field E is the vector sum of EA and EB: E = = EA EA + + EB. As illustrated in Figure 18.18, EA and EB are perpendicular, so E is the diagonal of the rectangle shown in the drawing. Thus, we can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the magnitude of E and trigonometry to find the directional angle q . EB. As illustrated in Figure 18.18, EA and EB are perpendicular, so E is the diagonal of the rectangle shown in the drawing. Thus, we can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the magnitude of E and trigonometry to find the directional angle q .
Solution
The magnitude of the net electric field is
The direction of E is given by the angle q in the drawing:
|
![]() =
=![]() 3.00 N/C directed to the right, and EB
3.00 N/C directed to the right, and EB![]() =
=![]() 2.00 N/C directed downward. Thus, EA and EB are perpendicular. What is the net electric field at P?
2.00 N/C directed downward. Thus, EA and EB are perpendicular. What is the net electric field at P?
![]() =
=![]() EA
EA![]() +
+![]() EB. As illustrated in Figure 18.18, EA and EB are perpendicular, so E is the diagonal of the rectangle shown in the drawing. Thus, we can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the magnitude of E and trigonometry to find the directional angle q .
EB. As illustrated in Figure 18.18, EA and EB are perpendicular, so E is the diagonal of the rectangle shown in the drawing. Thus, we can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the magnitude of E and trigonometry to find the directional angle q .