On earth a block has a weight of 88 N. This block is sliding on a horizontal surface on the moon, where the acceleration due
to gravity is 1.60 m/s
2. As Figure
4.38a shows, the block is being pulled by a horizontal rope in which the tension is
T = 24 N. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface is μ
k = 0.20. Determine the acceleration of the block.
 |
 |
|
|
 |

|
Figure 4.38 |
 |
|
(a)
|
A block is sliding on a horizontal surface on the moon. The tension in the rope is 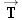 .
|
 |
|
(b)
|
The free-body diagram for the block, including a kinetic frictional force 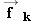 .
|
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
Solution
Figure
4.38b shows the free-body diagram for the block. The net force along the
x axis is Σ
Fx = +
T -
fk, where
T is the magnitude of the tension in the rope and
fk is the magnitude of the kinetic frictional force. According to Equation
4.8,
fk is related to the magnitude
FN of the normal force by
fk = μ
kFN, where μ
k is the coefficient of kinetic friction. The acceleration
ax of the block is given by Newton's second law as
We can obtain an expression for
FN by noting that the block does not move in the
y direction, so
ay = 0 m/s
2. Therefore, the net force Σ
Fy along the
y direction must also be zero. An examination of the free-body diagram reveals that Σ
Fy = +
FN -
mgmoon = 0, so that
FN =
mgmoon. The acceleration in the
x direction becomes
Using the earth-weight of the block to determine its mass, we find
The acceleration of the block is, then,



