| 3.6 |
The Chain Rule and Inverse Functions
|
In this section we will use the chain rule to calculate the derivatives of fractional powers, logarithms, exponentials, and
the inverse trigonometric functions.5 The same method is used to obtain a formula for the derivative of a general inverse function.
Finding the Derivative of an Inverse Function: Derivative of 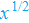
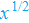
Earlier we calculated the derivative of 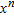 with
with 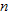 an integer, but we have been using the result for non-integral values of
an integer, but we have been using the result for non-integral values of 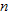 as well. We now confirm that the power rule holds for
as well. We now confirm that the power rule holds for  by calculating the derivative of
by calculating the derivative of  using the chain rule. Since
using the chain rule. Since
the derivative of 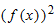 and the derivative of
and the derivative of  must be equal, so
must be equal, so
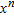 with
with 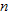 an integer, but we have been using the result for non-integral values of
an integer, but we have been using the result for non-integral values of 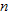 as well. We now confirm that the power rule holds for
as well. We now confirm that the power rule holds for 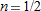 by calculating the derivative of
by calculating the derivative of  using the chain rule. Since
using the chain rule. Since
|
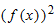 and the derivative of
and the derivative of  must be equal, so
must be equal, so
|
We can use the chain rule with 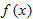 as the inside function to obtain:
as the inside function to obtain:
Solving for 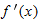 gives
gives
or
A similar calculation can be used to obtain the derivative of 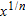 where
where 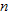 is a positive integer.
is a positive integer.
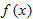 as the inside function to obtain:
as the inside function to obtain:
|
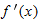 gives
gives
|
|
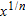 where
where 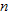 is a positive integer.
is a positive integer.
Derivative of 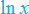
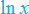
We use the chain rule to differentiate an identity involving 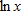 . Since
. Since  , we have
, we have
Solving for 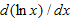 gives
gives
so
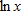 . Since
. Since  , we have
, we have
|
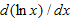 gives
gives
|
|
|
Derivative of 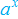
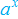
In Section 3.2, we saw that the derivative of 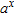 is proportional to
is proportional to 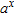 . Now we see another way of calculating the constant of proportionality. We use the identity
. Now we see another way of calculating the constant of proportionality. We use the identity
Differentiating both sides, using 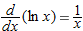 and the chain rule, and remembering that ln
and the chain rule, and remembering that ln 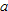 is a constant, we obtain:
is a constant, we obtain:
Solving gives the result we obtained earlier:
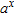 is proportional to
is proportional to 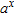 . Now we see another way of calculating the constant of proportionality. We use the identity
. Now we see another way of calculating the constant of proportionality. We use the identity
|
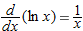 and the chain rule, and remembering that ln
and the chain rule, and remembering that ln 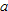 is a constant, we obtain:
is a constant, we obtain:
|
|
Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
In Section 1.5 we defined arcsin  as the angle between
as the angle between  and
and 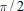 (inclusive) whose sine is
(inclusive) whose sine is  . Similarly,
. Similarly, 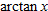 as the angle strictly between
as the angle strictly between  and
and 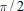 whose tangent is
whose tangent is  . To find
. To find  we use the identity
we use the identity  . Differentiating using the chain rule gives
. Differentiating using the chain rule gives
so
 as the angle between
as the angle between  and
and 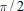 (inclusive) whose sine is
(inclusive) whose sine is  . Similarly,
. Similarly, 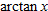 as the angle strictly between
as the angle strictly between  and
and 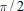 whose tangent is
whose tangent is  . To find
. To find  we use the identity
we use the identity  . Differentiating using the chain rule gives
. Differentiating using the chain rule gives
|
|
Using the identity  , and replacing θ by
, and replacing θ by 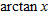 , we have
, we have
Thus we have
By a similar argument, we obtain the result:
 , and replacing θ by
, and replacing θ by 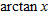 , we have
, we have
|
|
|
|
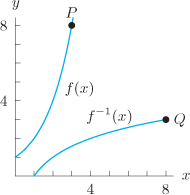
Derivative of a General Inverse Function
Each of the previous results gives the derivative of an inverse function. In general, if a function 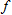 has a differentiable inverse,
has a differentiable inverse,  , we find its derivative by differentiating
, we find its derivative by differentiating 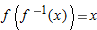 by the chain rule:
by the chain rule:
so
Thus, the derivative of the inverse is the reciprocal of the derivative of the original function, but evaluated at the point
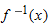 instead of the point
instead of the point  .
.
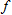 has a differentiable inverse,
has a differentiable inverse,  , we find its derivative by differentiating
, we find its derivative by differentiating 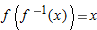 by the chain rule:
by the chain rule:
|
|
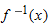 instead of the point
instead of the point  .
.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercises and Problems for Section 3.6
Exercises
For Exercises 1-41, find the derivative. It may be to your advantage to simplify before differentiating. Assume  , and
, and 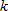 are constants.
are constants.
 , and
, and 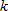 are constants.
are constants.
| 1. |
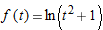 |
| 2. |
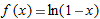 |
| 3. |
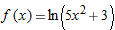 |
| 4. |
 |
| 5. |
 |
| 6. |
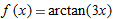 |
| 7. |
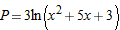 |
| 8. |
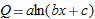 |
| 9. |
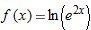 |
| 10. |
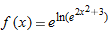 |
| 11. |
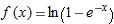 |
| 12. |
 |
| 13. |
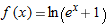 |
| 14. |
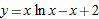 |
| 15. |
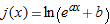 |
| 16. |
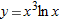 |
| 17. |
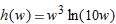 |
| 18. |
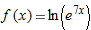 |
| 19. |
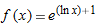 |
| 20. |
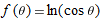 |
| 21. |
 |
| 22. |
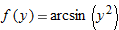 |
| 23. |
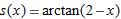 |
| 24. |
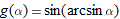 |
| 25. |
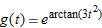 |
| 26. |
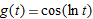 |
| 27. |
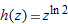 |
| 28. |
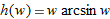 |
| 29. |
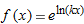 |
| 30. |
 |
| 31. |
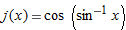 |
| 32. |
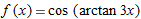 |
| 33. |
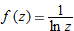 |
| 34. |
 |
| 35. |
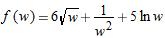 |
| 36. |
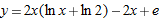 |
| 37. |
 |
| 38. |
 |
| 39. |
 |
| 40. |
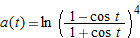 |
| 41. |
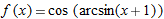 |
Problems
| 42. |
Let
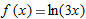 . .
|
| 43. |
On what intervals is
 concave up? concave up?
|
| 44. |
Use the chain rule to obtain the formula for
 . .
|
| 45. |
Using the chain rule, find
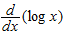 . (Recall . (Recall 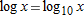 .) .)
|
| 46. |
To compare the acidity of different solutions, chemists use the pH (which is a single number, not the product of
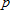 and and 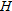 ). The pH is defined in terms of the concentration, ). The pH is defined in terms of the concentration,  , of hydrogen ions in the solution as , of hydrogen ions in the solution as
|
| 47. |
The number of years,
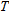 , it takes an investment of $1000 to grow to , it takes an investment of $1000 to grow to  in an account which pays 5% interest compounded continuously is given by in an account which pays 5% interest compounded continuously is given by
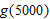 and and 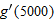 . Give units with your answers and interpret them in terms of money in the account. . Give units with your answers and interpret them in terms of money in the account.
|
| 48. |
A firm estimates that the total revenue,
 , in dollars, received from the sale of , in dollars, received from the sale of 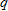 goods is given by goods is given by
 , is the rate of change of the total revenue as a function of quantity. Calculate the marginal revenue when , is the rate of change of the total revenue as a function of quantity. Calculate the marginal revenue when 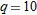 . .
|
| 49. |
|
| 50. |
Find the equation of the best quadratic approximation to
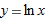 at at 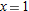 . The best quadratic approximation has the same first and second derivatives as . The best quadratic approximation has the same first and second derivatives as 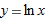 at at 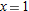 . .
|
| 51. |
|
| 52. |
Imagine you are zooming in on the graph of each of the following functions near the origin:
|
|
||||||||
|
| 53. |
 |
| 54. |
 |
| 55. |
 |
| 56. |
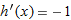 |
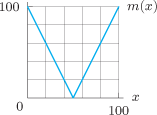
In Problems 57-59, use Figure 3.31 to estimate the derivatives.
|
||||||||
|
| 57. |
 |
| 58. |
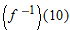 |
| 59. |
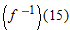 |
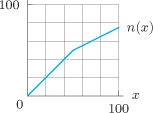
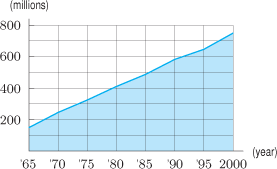
In Problems 60-62, use Figure 3.32 to calculate the derivative.
|
||
|
| 60. |
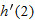 if if 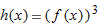 |
| 61. |
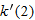 if if 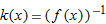 |
| 62. |
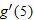 if if 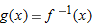 |
| 63. |
|
| 64. |
|
| 65. |
Use the table and the fact that
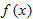 is invertible and differentiable everywhere to find is invertible and differentiable everywhere to find 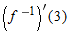 . .
|
| 66. |
At a particular location,
 is the number of gallons of gas sold when the price is is the number of gallons of gas sold when the price is 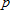 dollars per gallon. dollars per gallon.
|
| 67. |
|
| 68. |
| 69. |
|
| 70. |
If
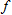 is increasing and is increasing and 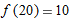 , which of the two options, (a) or (b), must be wrong? , which of the two options, (a) or (b), must be wrong?
|
| 71. |
An invertible function
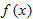 has values in the table. Evaluate has values in the table. Evaluate
|
| 72. |
If
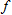 is continuous, invertible, and defined for all is continuous, invertible, and defined for all  , why must at least one of the statements , why must at least one of the statements 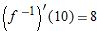 , , 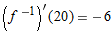 be wrong? be wrong?
|
| 73. |
|
Strengthen Your Understanding
In Problems 74-76, explain what is wrong with the statement.
| 74. |
If
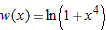 then then 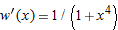 . .
|
| 75. |
The derivative of
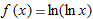 is is
|
| 76. |
Given
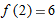 , ,  , and , and  , we have , we have
|
In Problems 77-80, give an example of:
| 77. |
A function that is equal to a constant multiple of its derivative but that is not equal to its derivative.
|
| 78. |
A function whose derivative is
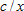 , where c is a constant. , where c is a constant.
|
| 79. |
A function
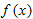 for which for which  , where , where 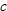 is a constant. is a constant.
|
| 80. |
A function
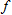 such that such that  . .
|
Are the statements in Problems 81-82 true or false? Give an explanation for your answer.
| 81. |
The graph of
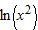 is concave up for is concave up for 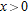 . .
|
| 82. |
If
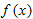 has an inverse function, has an inverse function,  , then the derivative of , then the derivative of  is is 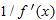 . .
|

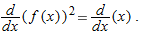
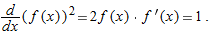
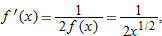


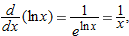
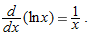
 .
.
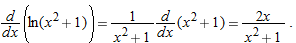
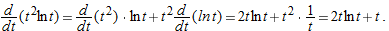
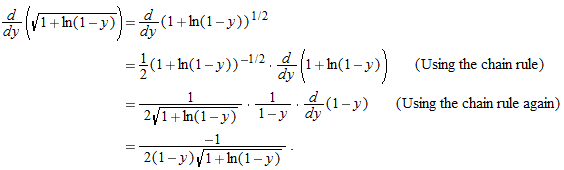

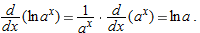
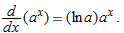
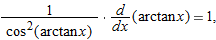
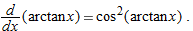
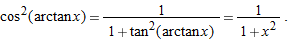


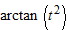
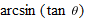 .
.
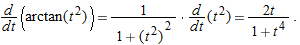
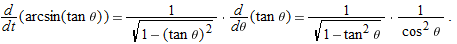

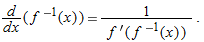
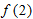

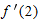
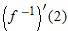
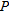 and
and 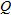 .
.
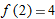 .
.
 .
.
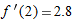 .
.
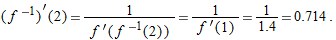
 .
.
 and
and 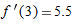 , so the equation of the tangent line at
, so the equation of the tangent line at 
 , so the slope at
, so the slope at 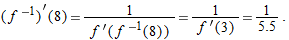
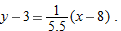
 and
and 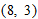 are reflections of one another in the line
are reflections of one another in the line 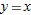 . Thus, the two tangent lines are reflections of one another in the line
. Thus, the two tangent lines are reflections of one another in the line 
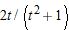

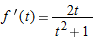 .
.
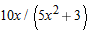

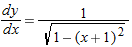 .
.
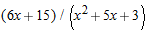
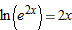 , the derivative
, the derivative 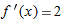 .
.
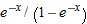

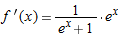 .
.
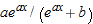
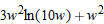
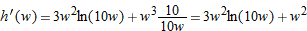 .
.

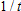
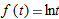 (because
(because 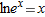
 ), so
), so 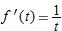 .
.
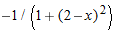
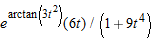
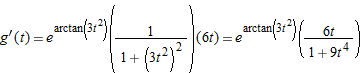 .
.
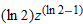
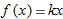 so,
so, 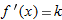 .
.
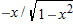
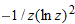
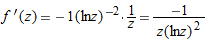
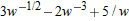

 .
.

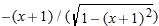
 .
.
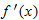 and simplify your answer.
and simplify your answer.


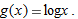

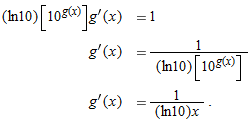



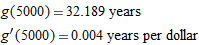
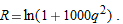
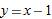
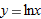 , we have
, we have 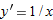 , so the slope of the tangent line is
, so the slope of the tangent line is  . The equation of the tangent line is
. The equation of the tangent line is 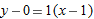 , so, on the tangent line,
, so, on the tangent line, 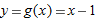 .
.
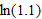 and
and 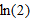 .
.
 , we have
, we have


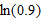 and
and 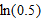 ? Why?
? Why?
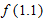 and
and  . Similarly,
. Similarly, 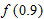 and
and 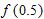 are also below
are also below 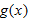 . This is true for any approximation of this function by a tangent line since
. This is true for any approximation of this function by a tangent line since 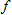 is concave down
is concave down 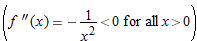 . Thus, for a given
. Thus, for a given  -value, the
-value, the  -value given by the function is always below the value given by the tangent line.
-value given by the function is always below the value given by the tangent line.
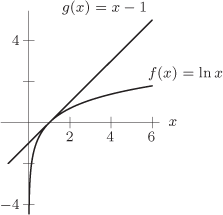
 .
.

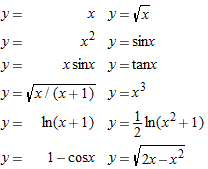
 has the given derivative.
has the given derivative.

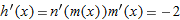 we must find values
we must find values 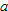 and
and 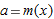 and
and 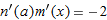 .
.
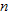 gives
gives
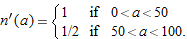
 gives
gives

 are 1 and
are 1 and  and the only values of the derivative
and the only values of the derivative  are 2 and
are 2 and 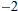 . In order to have
. In order to have 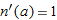 and
and 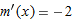 . Thus
. Thus 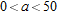 and
and  .
.
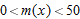 for
for 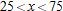 .
.
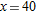 .
.

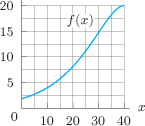
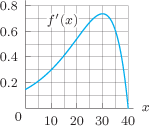
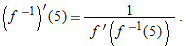
 . From the graph of
. From the graph of 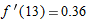 . Thus
. Thus 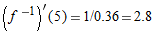 .
.
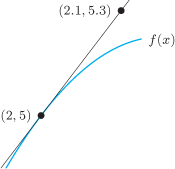
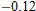
 . The point (2.1, 5.3) is on the tangent line, so
. The point (2.1, 5.3) is on the tangent line, so
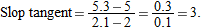
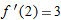 .
.
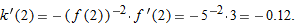
 , find
, find 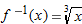
 .
.
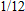
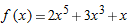 , find
, find 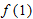 .
.
 .
.
 .
.
 , we first look in the table to find that
, we first look in the table to find that  , so
, so 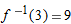 . Thus,
. Thus,
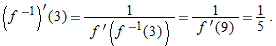
 tell you about gas sales?
tell you about gas sales?
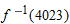 .
.
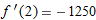 tell you about gas sales?
tell you about gas sales?

 give the US population
give the US population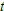 .
.
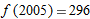 tell you about the US population?
tell you about the US population?
 . Give units.
. Give units.
 tell you about the population? Give units.
tell you about the population? Give units.

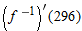 . Give units.
. Give units.
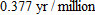
 , in millions, registered in the world
, in millions, registered in the world 
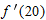


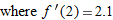 ,
, 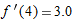 ,
,  ,
, 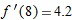 , find
, find 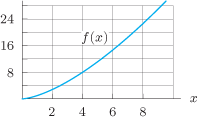

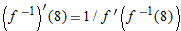 . From the graph we see
. From the graph we see  . Thus
. Thus 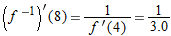 .
.
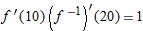 .
.
 .
.
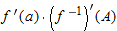
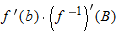

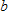

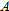


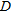
 by identifying the limit as the derivative of
by identifying the limit as the derivative of 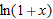 at
at 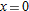 .
.
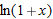 at
at 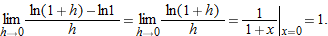
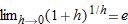 .
.
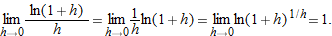
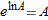 , we have
, we have
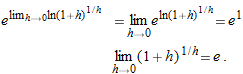
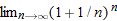 .
.

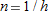 . Then as
. Then as 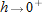 , we have
, we have 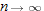 . Since
. Since

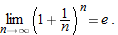
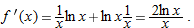
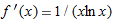
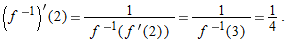
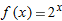
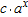 with
with 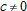 ,
,  and
and 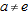 is a constant multiple of its derivative but it is not equal to its derivative:
is a constant multiple of its derivative but it is not equal to its derivative: 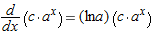 . One example is
. One example is 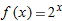 .
.
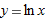
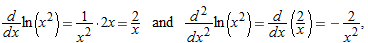
 is negative for
is negative for