Uniform circular motion. A particle undergoes uniform circular motion on a horizontal xy plane. At time 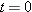 , it moves through coordinates (3.0 m, 0) with velocity 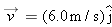 . At 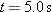 , it moves through (11.0 m, 0) with velocity 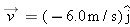 . In unit vector notation, what is its acceleration at 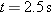 ?
In uniform circular motion, a particle follows a circular path at constant speed v, has a velocity 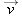 tangent to the circle, and has an acceleration directed toward the center with a magnitude given by Eq. 4-34 tangent to the circle, and has an acceleration directed toward the center with a magnitude given by Eq. 4-34 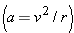 . .
Calculations: Because the two given velocity vectors are in opposite directions, they must be on opposite sides of the circular path. Because the vectors are tangent to the circle and directed parallel to the y axis, they must be on the left side and right side of the circle. Thus at 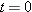 , the particle is on the left side at coordinates (3.0 m, 0), as indicated in Fig. 4-H. At 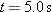 , it is on the right side at coordinates (11.0 m, 0). The center of the circle must be midway between these points, at coordinates (7.0 m, 0), which means the radius is 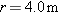 .
The speed is the magnitude of 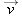 , which is 6.0 m/s. We then have
At 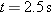 , the particle is at the top of the circle, midway between the left side and the right side, and thus it must be at coordinates (7.0 m, 4.0 m). Because the acceleration vector is always directed toward the center of the circle, at 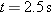 it must be directed down toward (7.0 m, 0). Therefore,
|