Two people pull on a horizontal spring that is attached to an immovable wall. Then, they detach it from the wall and pull on opposite ends of the horizontal spring. They pull just as hard in each case. In which situation, if either, does the spring stretch more? Account for your answer.
The drawing shows identical springs that are attached to a box in two different ways. Initially, the springs are unstrained. The box is then pulled to the right and released. In each case the initial displacement of the box is the same. At the moment of release, which box, if either, experiences the greater net force due to the springs? Provide a reason for your answer.
In Figures 10.11 and 10.14, the shadow moves in simple harmonic motion. Where on the shadow’s path is (a) the velocity equal to zero and (b) the acceleration equal to zero?
A steel ball is dropped onto a concrete floor. Over and over again, it rebounds to its original height. Is the motion simple harmonic motion? Justify your answer.
Ignoring the damping introduced by the shock absorbers, explain why the number of passengers in a car affects the vibration frequency of the car’s suspension system.
Review Conceptual Example 8 before answering this question. A block is attached to a horizontal spring and slides back and forth in simple harmonic motion on a frictionless horizontal surface. A second identical block is suddenly attached to the first block. The attachment is accomplished by joining the blocks at one extreme end of the oscillation cycle. The velocities of the blocks are exactly matched at the instant of joining. Explain how (a) the amplitude, (b) the frequency, and (c) the maximum speed of the oscillation change.
A particle is oscillating in simple harmonic motion. The time required for the particle to travel through one complete cycle is equal to the period of the motion, no matter what the amplitude is. But how can this be, since larger amplitudes mean that the particle travels farther? Explain.
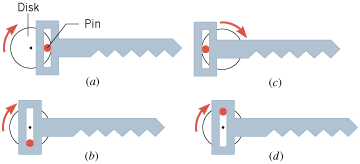
An electric saber saw consists of a blade that is driven back and forth by a pin mounted on the circumference of a rotating circular disk. As the disk rotates at a constant angular speed, the pin engages a slot and forces the blade back and forth, in the sequence (a), (b), (c), and (d) shown in the drawing. Is the motion of the blade simple harmonic motion? Explain.
Is more elastic potential energy stored in a spring when the spring is compressed by one centimeter than when it is stretched by the same amount? Explain.
Suppose that a grandfather clock (a simple pendulum) is running slowly. That is, the time it takes to complete each cycle is longer than it should be. Should one shorten or lengthen the pendulum to make the clock keep the correct time? Why?
Consult Concept Simulation 10.2 to review the concept that lies at the heart of the answer to this question. In principle, the motion of a simple pendulum and an object on an ideal spring can both be used to provide the basic time interval or period used in a clock. Which of the two kinds of clocks becomes more inaccurate when carried to the top of a high mountain? Justify your answer.
Concept Simulation 10.2 deals with the concept on which this question is based. Suppose you were kidnapped and held prisoner by space invaders in a completely isolated room, with nothing but a watch and a pair of shoes (including shoelaces of known length). Explain how you might determine whether this room is on earth or on the moon.
Two people are sitting on playground swings. One person is pulled back 4° from the vertical and released, while the other is pulled back 8° from the vertical and released. If the two swings are started together, will they both come back to the starting points at the same time? Justify your answer.
A car travels over a road that contains a series of equally spaced bumps. Explain why a particularly jarring ride can result if the horizontal velocity of the car, the bump spacing, and the oscillation frequency of the car’s suspension system are properly “matched.”
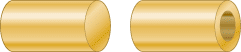
The drawing shows two cylinders. They are identical in all respects, except one is hollow. In a setup like that in Figure 10.29, identical forces are applied to the right end of each cylinder. Which cylinder, if either, stretches the most? Why?
Young’s modulus for steel is thousands of times greater than that for rubber. All other factors being equal, does this mean that steel stretches much more easily than rubber? Explain.
A trash compactor crushes empty aluminum cans, thereby reducing the total volume of the cans by 75%. Can the value given in Table 10.3 for the bulk modulus of aluminum be used to calculate the change in pressure generated in the trash compactor? Give a reason for your answer.
Both sides of the relation F =
= S(DX/L0)A (Equation 10.18) can be divided by the area A to give F/A on the left side. Why can’t this F/A term be called a pressure, such as the pressure that appears in DP
S(DX/L0)A (Equation 10.18) can be divided by the area A to give F/A on the left side. Why can’t this F/A term be called a pressure, such as the pressure that appears in DP =
= –B (DV/V0) (Equation 10.20)?
–B (DV/V0) (Equation 10.20)?
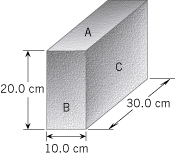
The block in the drawing rests on the ground. Which face, A, B, or C, experiences (a) the largest stress and (b) the smallest stress when the block is resting on it? Explain.
 |
| Copyright © 2000-2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. or related companies. All rights reserved. |
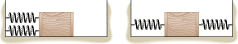
![]() =
=![]() S(DX/L0)A (Equation 10.18) can be divided by the area A to give F/A on the left side. Why can’t this F/A term be called a pressure, such as the pressure that appears in DP
S(DX/L0)A (Equation 10.18) can be divided by the area A to give F/A on the left side. Why can’t this F/A term be called a pressure, such as the pressure that appears in DP![]() =
=![]() –B (DV/V0) (Equation 10.20)?
–B (DV/V0) (Equation 10.20)?